Record-breaking rain more likely due to climate change
Author: Press Office
11:12 (UTC) on Thu 11 Mar 2021
Record-breaking rainfall like that seen on 3 October 2020 could be 10 times more likely by 2100.
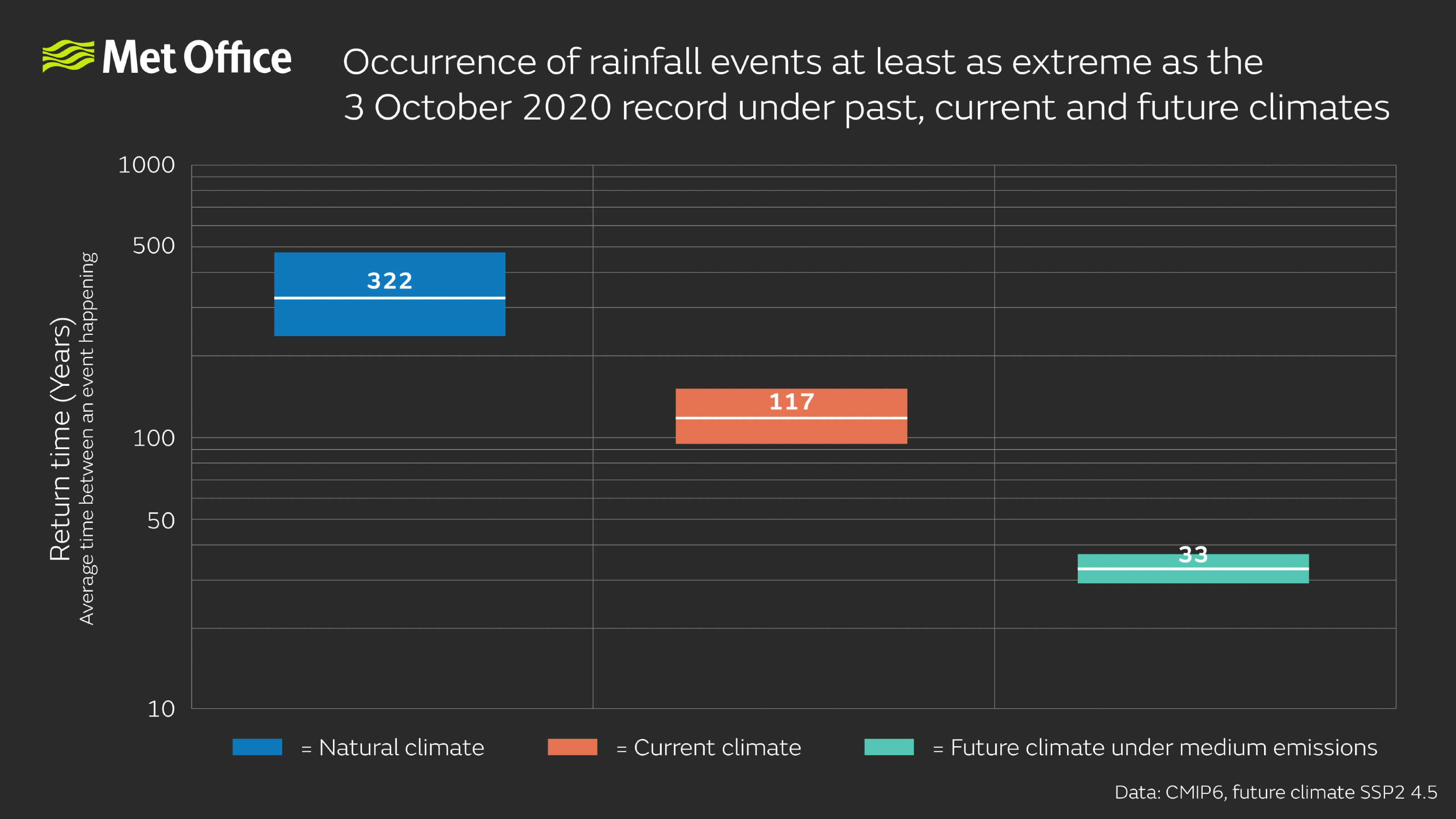
A new study by scientists in the Met Office Hadley Centre has found that days with extreme rainfall accumulations will become more frequent through the century. The research used the record rainfall observed on 3 October 2020 as an example and found that while in a natural environment, with no influence from human induced climate change, an event similar or more extreme would be a 1 in 300 year event, it is now a 1 in 100 year event in the current climate. By 2100 under a medium emissions scenario (SSP2 4.5) that level of extreme daily rainfall could be seen every 30 years, making it 10 times more likely than in a natural environment.
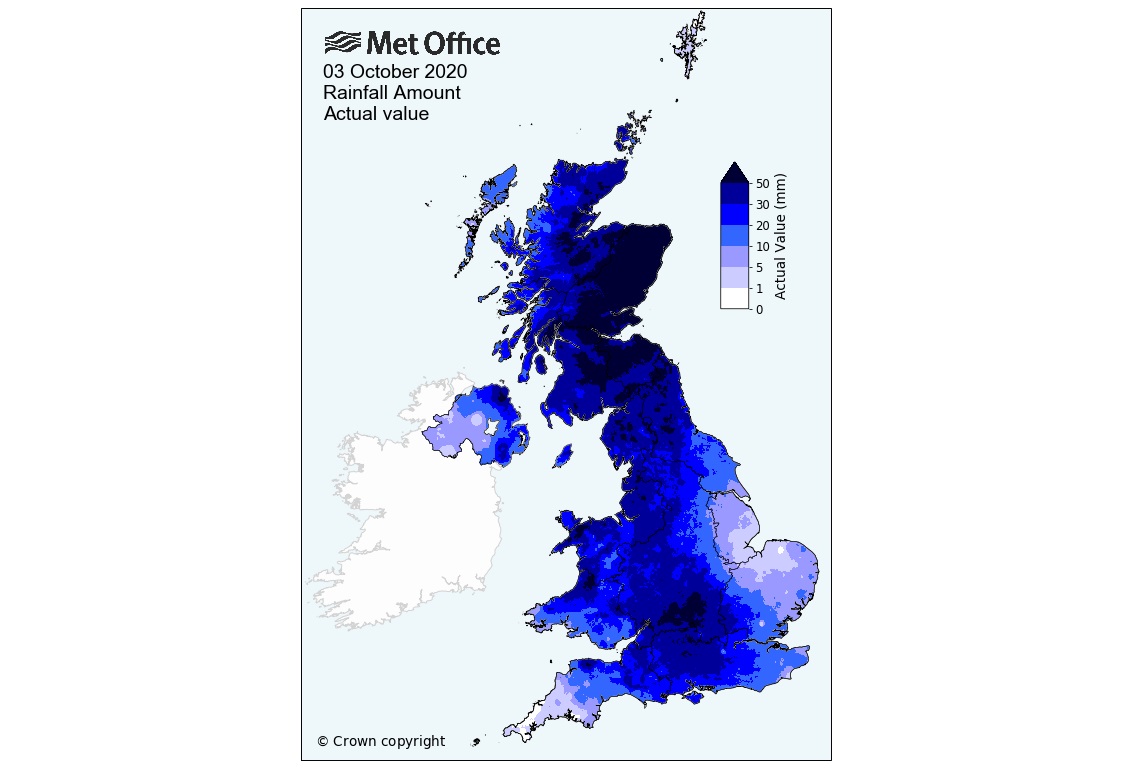
In addition to increased frequency of these extreme events, the research found that 3 October 2020 was provisionally the UK’s wettest day in a daily series stretching back to 1891. The rainfall was very widespread resulting in provisional average rainfall across the entire UK of 31.7mm, or to put it another way, if expressed as the volume of rain that is more than the capacity of Loch Ness – the largest lake in the UK by volume at 7.4 cubic kilometres of water.
The rainfall on 3 October followed on from Storm Alex, which caused disruption across Europe, especially south-east France and north-west Italy.
Head of the Met Office’s National Climate Information Centre, Mark McCarthy, said: “The record daily UK rainfall recorded on 3 October 2020 in the wake of Storm Alex was really quite extreme. The preceding drier conditions through September helped prevent significant widespread impacts but an event like this has the potential to cause damaging effects to infrastructure and services.”
Lead author of the paper Dr Nikos Christidis, Senior Climate Scientist in the Met Office Hadley Centre, said: “Our study shows that in a medium emissions scenario these sorts of rainfall extremes could become much more frequent, reinforcing the need to plan for the consequences of a warming global climate. We are also now starting to see how more frequent extreme rainfall events are already impacting the UK, showing that human induced climate change is already having an impact on the weather we experience in the UK.”
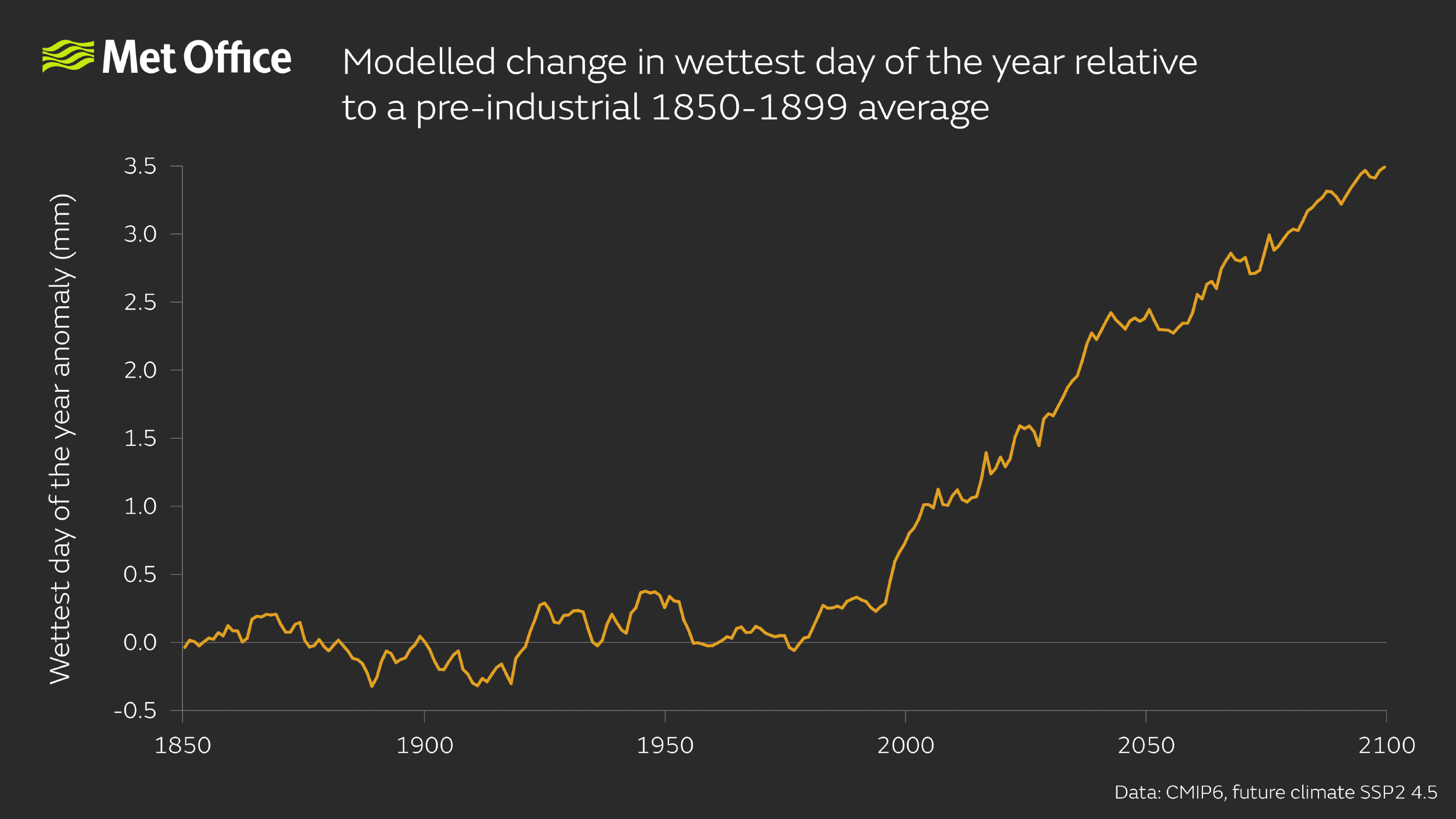
The analysis from the study adds to the existing evidence of human influence leading to more extreme rainfall in the UK and that in recent decades an increase in the frequency of extreme rainfall events in the UK has become more prominent. Furthermore, this is the first event attribution study to examine changes in the wettest day of the year and establish that despite the large variability, a signal of more frequent extremes has emerged and will continue to intensify in coming decades.
Previously any signal of human-induced climate change impacting rainfall has typically been hard to detect due to its significant variability, especially compared to temperature. A Met Office paper in 2018 suggested any signal would first be seen in rainfall extremes.
In addition to increased frequency of these extreme events, the research found that human-induced climate change has and will continue to result in more variation in rainfall across the UK. This means that rather than many moderate rain events, we are more often seeing very wet or very dry spells.
In a warming climate the atmosphere can hold more water, and wet extremes would therefore be expected to become more intense. This increase in rainfall extremes in the UK is consistent with the headline findings from the UKCP18 climate projections.
Understanding the underpinning role of anthropogenic climate change and how it might alter the frequency of extreme rainfall events is crucial, in order to help communities and policy makers effectively plan their adaptation and reduce their vulnerability.
The paper has been published in Atmospheric Science Letters.





